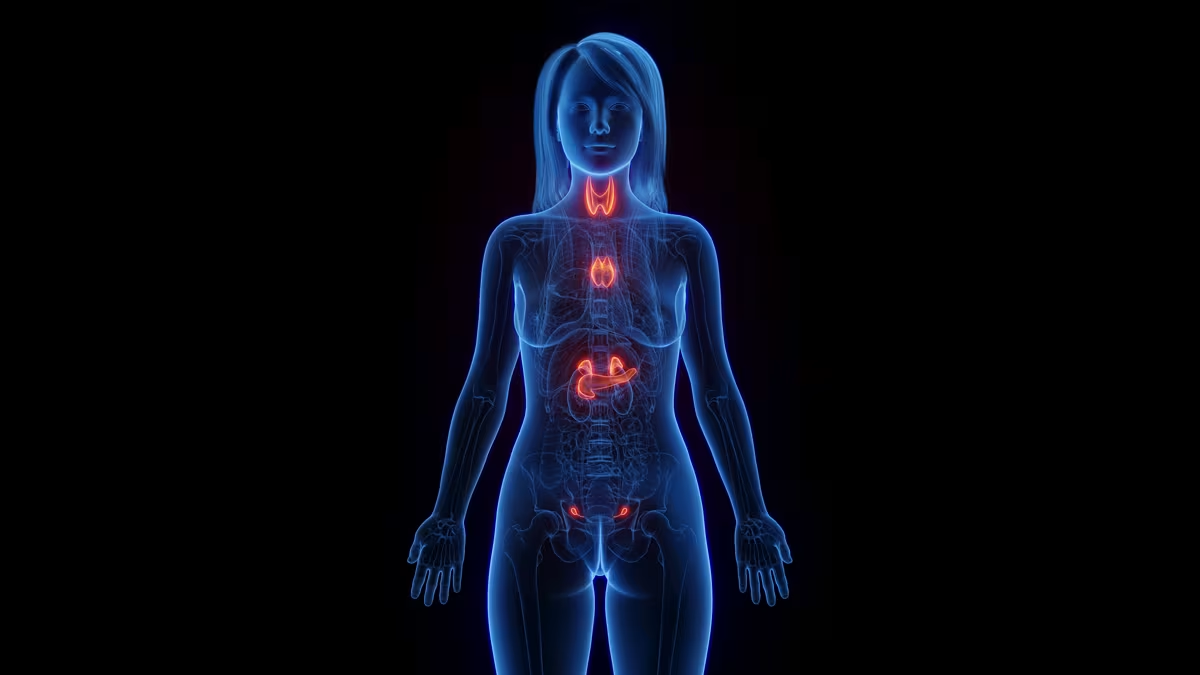
The endocrine system is a series of glands responsible for creating and distributing hormones throughout the body, chemical messengers of sorts. This important system plays a role in many bodily functions, including regulating metabolism, impacting growth and development, and sexual function and reproduction. The hormones produced by this system can also impact the development and progression of breast cancer. Here, we’ll explore the relationship between the two and ways in which endocrine therapy can help improve outcomes for some breast cancer patients.
What Is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a series of glands and organs throughout the body that produce and manage the storage and release of more than 50 hormones.1 These hormones are involved in the control of many bodily functions, including metabolism, mood, the sleep-wake cycle, and reproduction. In addition to the pancreas, thyroid gland and adrenal glands, the testes and ovaries are part of the male and female endocrine systems, respectively.2
Reproductive Hormones Produced by the Endocrine System
Important to the development of breast cancer, the hormones estrogen and progesterone are produced by the endocrine system. Although found at higher levels in women, estrogen and progesterone are also present in men. These important reproductive hormones are involved in puberty, influence fertility, help maintain bone and skin health, and mood regulation. They play an important role throughout our life, from puberty through menopause and beyond. Unfortunately, in some cases a hormonal imbalance or prolonged exposure to these hormones can increase the risk of developing hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.3
Hormones and Breast Cancer Cells
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers diagnosed among females in the United States, with 1 in 8 women being diagnosed.5 Although significantly less common, men can also develop breast cancer. Breast cancer is a diverse disease with many different types, classified based on where the cancer starts, its growth patterns, and whether it is influenced by hormones.6
Breast cancers that are influenced by estrogen and/or progesterone are categorized as hormone receptor positive breast cancer. These tumors have estrogen receptors (ER-positive) and/or progesterone receptors (PR-positive) on the surface of the cancer cells, and the presence of these hormones in the body feeds the growth of the tumor.7
Not all breast cancers are hormone receptor (HR) positive. Testing done at the time of biopsy and/or surgery can check for the presence of estrogen and progesterone receptors and determine whether it is HR-positive. This is an important part of the breast cancer work up as HR-positive cancers are often treated with endocrine therapies.
Endocrine Therapies and Breast Cancer
For breast cancers categorized as HR-positive, a component of the treatment will often include an endocrine therapy. These medications work by targeting and manipulating the levels of estrogen and progesterone that fuel the growth of the tumor. By blocking hormone receptors on the cancer cells or reducing production of the hormones themselves, this type of treatment can help to prevent the cancer from growing, recurring, or spreading.8
There are several classes of endocrine therapies, and the decision of which to use can be based on several factors but is largely influenced by menopausal status. For premenopausal women, endocrine therapies aim to block estrogen with a medication called tamoxifen, which may also be given with ovarian suppression medications which stop the ovaries from producing estrogen. For postmenopausal women, aromatase inhibitors are the primary treatment option, reducing the levels of estrogen in the body.9
Endocrine therapy is an important treatment option for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. While hormone therapy is generally effective, it may come with side effects, so it’s important to discuss potential risks and benefits with your care team.
Taking a Proactive Approach to Your Health
The sooner breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the outcomes. With the advance of treatment, including endocrine therapies, breast cancer diagnosed at an early stage can have very good outcomes.10
Be sure to schedule regular check-ups with your care team, perform breast self-exams at least once a month, and get an annual mammogram beginning at age 40. Early detection leads to early intervention and better outcomes.11
SOURCES:
- Cleveland Clinic. Hormones.
- Endocrine Society. Hormones and Breast Cancer.
- American Cancer Society. (2020). Breast cancer risk factors.
- National Breast Cancer Foundation, Inc. Breast Cancer Facts and Stats.
- American Cancer Society. Types of Breast Cancer.
- American Cancer Society. What Causes Breast Cancer?
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.
- National Cancer Institute. (2022). Hormone therapy for breast cancer.
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Endocrine therapy for breast cancer.
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Breast cancer survival rates.
- American Cancer Society. (2022). Breast cancer early detection and diagnosis.



